Complex Hernia and Prehabilitation of the Abdominal Wall
June 19, 2025 –![]() Ernesto Escobar, MD
Ernesto Escobar, MD
A practical way to define a complex hernia is one that cannot be treated using conventional methods (standard open or laparoscopic surgery) because the edges of the defect cannot be closed.
1. History of complicated intra-abdominal disease (such as perforated appendicitis, perforated ulcers, intestinal infarction, abdominal trauma — including stab wounds, gunshot wounds, accidents, or blunt trauma) or surgery in a patient with poor nutritional status who later develops a hernia.
2. Obesity
3. Chronic diseases that impair wound healing
4. Surgical site infections that result in wound dehiscence.
Due to the complexity of these cases, achieving a successful repair requires several key steps:
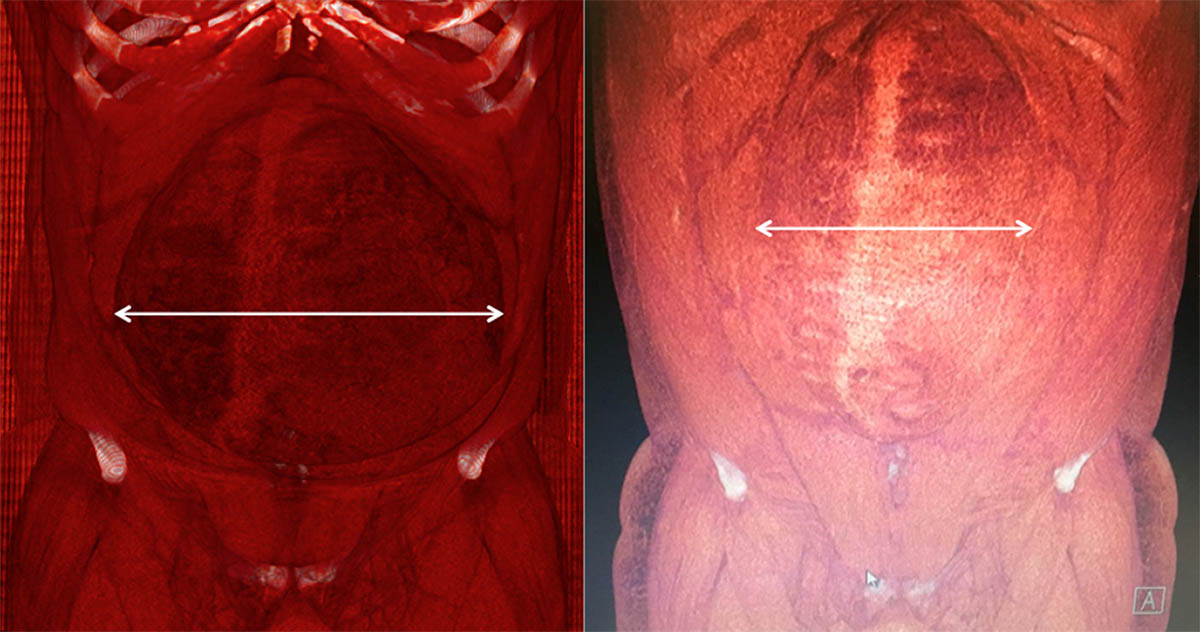
a. Proper evaluation of the hernia, usually through a CT scan
b. Assessment of the patient’s overall health
c. Management of conditions that may impair healing (diabetes, smoking, malnutrition, obesity)
d. Abdominal Wall Prehabilitation**
With this last point—Abdominal Wall Prehabilitation—we will highlight two major techniques that contribute to a successful closure of the hernia defect:
1. Botulinum Toxin Injection
2. Progressive Pneumoperitoneum
Botulinum Toxin Injection
Botulinum toxin has been widely used for cosmetic purposes in Plastic Surgery, Dermatology, and Aesthetic Medicine under various brand names (Dysport, Botox, Xeomin, Allergan, Azalure, Jeuveau, Myobloc/Neurobloc, Bocouture, Cbtx a/prosigne®/lantox, Daxxify, HUGEL, Ipsen, Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA, Neuronox, Vistabel, etc.).
When Botulinum Toxin is injected into the abdominal muscles, they relax, making it easier to close the hernia during surgery. This reduces the likelihood of hernia recurrence in the future.
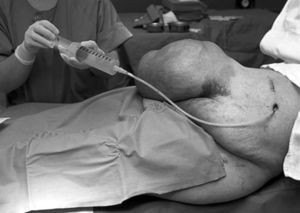
Progressive Pneumoperitoneum
To insufflate air into the cavity, a plastic catheter must be placed and left in position for several days. The patient must attend follow-up visits with the surgeon for the gradual introduction of gas.
After several sessions, the patient will be ready to undergo the surgical procedure.
These techniques (botulinum toxin and progressive pneumoperitoneum) are reserved for complex hernias and are not routinely used for all types of hernias.
Support from the multidisciplinary team and optimization of the patient’s health status, as well as prehabilitation measures, will help ensure a successful treatment.
